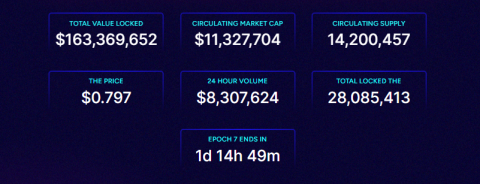
Sei Network and Ecosystem Overview
Let's learn about Sei Blockchain - a layer 1 chain focusing on trading. Dubbed “Decentralized NASDAQ” as it focuses on providing CeFi trading experience with DeFi tools.

Evmos is a proof-of-stake (PoS) network that allows the transfer of value between the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems . It is developed using the Cosmos software development kit (SDK). Developers can seamlessly leverage Evmos to run Ethereum smart contracts on application-specific Cosmos networks. In addition, the Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol allows Evmos to link decentralized applications (Dapps) on different blockchains and benefit from common liquidity and value transfer.
Evmos uses Tendermint Core's Byzantine Fault Tolerance to distinguish itself from other application classes. By combining the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Cosmos, Evmos also allows developers to create cross-chain Dapps faster and more cost-effectively. All in all, Evmos strives to give Tendermint developers a perfect experience using Ethereum tools by providing them with an open source library to support EVM compatibility across the ecosystem. Cosmos.
The EVMOS token is important in securing the Evmos blockchain by incentivizing developers and validating the network. In addition to driving network transactions and validation processes, EVMOS is the second asset on EVM that facilitates network participation through governance voting. As an EVMOS token holder, you are responsible for navigating the Evmos Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and shaping the future of the ecosystem.

DeFi applications can be developed on the Ethereum blockchain due to its maturity and wide user base, but lagging leads to high operating costs and slow transaction speeds. EVM-compatible Layer 1 chains, like Evmos, allow developers to distribute Ethereum applications to a larger user base, further increasing the utility of the application.
Earlier, the article mentioned that Evmos is built using the Cosmos SDK. The SDK is a tool for developing a PoS or Proof-of-Authority (PoA) network. It uses a flexible framework instead of a virtual machine-oriented framework. Mastering the differences between those two frameworks will allow you to understand why the Cosmos SDK is ideal for developing interoperable specific networks of applications.
In a decentralized blockchain with several nodes like Evmos, the nodes act like generals. As a result, Evmos can continue to run even if some nodes fail or behave maliciously. Currently, almost all Bitcoin wallets rely on trusted servers to validate transactions because the PoW mechanism requires waiting for multiple confirmations before the transaction becomes irreversible. Unlike such systems, Evmos provides near-instant and secure mobile-based payment verification, realizing minimal and practical payments on mobile.
In the Ethereum whitepaper, the developers describe ETH as Ethereum's main internal cryptocurrency fuel for payment of transaction fees. The fuel concept is interesting from the perspective of controlling the scarcity of cubic space. However, the Evmos developers feel their project will significantly improve the concept, especially in regards to fostering more participation through balanced economics.
The Layer 1 chain basically has three network actors: Developers, users, and block proposers. Each plays an essential role in enhancing and preserving value for any blockchain. In general, block proposers receive more rewards than users and developers (the most active contributors).
In a nutshell, the EVMOS token will be used to:
Initially, the supply of EVMOS was capped at 200 million, assigned to network contributors, DAO treasury, and strategic reserve.
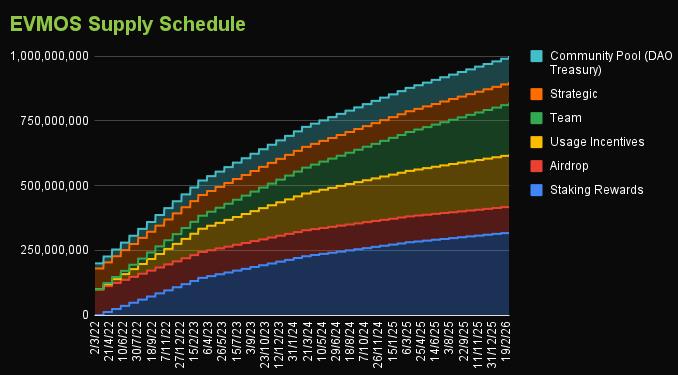
EVMOS is designed for high inflation, with around 300 million tokens issued in the first year. The tokens will be issued using an exponential dwindling schedule, which will help mitigate annual inflation. The project plans to issue a total of 1 billion tokens within 4 years in a process dubbed “The Half-Life”.
While this makes the project theoretically deflationary, the developers see EVMOS as an asset with an unrestricted supply. However, the team advises the community to vote for another token supply system after the first four years. For example, they may recommend a linear or constant system if the reward becomes too little.
In Evmos, the gas fee is not the amount of money burned but merely increasing the percentage of blockchain ownership by validators. The platform now splits fees as an incentive between developers and validators for their services through an inbuilt, reciprocal fee mechanism. This distributed revenue/fee mechanism is called The Dapp Store.
You can think of it as an app store, where some of the income from the sale of apps is allocated to the store operators and some to the developers.
The Store incentivizes developers based on the value and impact of their Dapps, rather than their ability to accelerate a new governance token. In this regard, developers building on Evmos get a real stake in the development and governance of the platform. Initially, fees are split 50/50 between implementers and validators but can be changed through a governance proposal.

It is important to note that transaction costs on the Cosmos blockchain are accrued with the block distribution token and are sent to network validators and block proposers. The block distribution does not include gas fees as they vary according to network activities and the gas price market.
Evmos plans to prioritize app incentives that will drive TVL as it is the ideal way to drive network growth. The concept is to assign more EVMOS tokens from the incentive pool to a protocol where users can lock their LP tokens in an ERC-20 form.
EVM holders can choose the application of the Evmos ecosystem, which is ideal for use in incentivizing farming. The model is simply a liquidity miner connected to the base layer but based on governance (like the distributed Avalanche Rush). The development team is estimated to hold 200 million EVMOS tokens within 4 years. Its scale is large because Evmos acknowledges its users as the mainstay of its success.
Validators and delegators are essential in securing the Evmos network by proposing and validating blocks. Their functions can grow to provide oracles, secure bridging, and provide aggregation services for Celestia and other Evmos side chains, making them core contributors. Initially, there are 150 active validators, but the number may be changed through a future governance vote.
32% of newly issued tokens are allocated to incentivize active validators and their delegators evenly based on their EVMOS stake. Validators charge the authorizer a small fee for the staking rewards they generate on their behalf. While validators can set different commission rates, Evmos allows a minimum rate of 5%.
The Evmos Validator can participate in the daily operation of the network by voting on proposals, including changes to network parameters and spending funds from the Evmos community team. Since Evmos uses a “one token, one vote” mechanism, holders can vote on governance proposals without special consideration for some votes. However, since proxies receive validators' votes, they are staking if they rarely vote themselves; validators are entitled to one dominant vote in the “one token, one vote” model.
Evmos has deployed Aave V3 on its network to extend lending to the Evmos ecosystem and the wider Cosmos world. As mentioned, Evmos acts as a gateway to the Cosmos world for users of Ethereum and other EVM chains. It achieves this through developer-focused incentives, interoperability on other Cosmos blockchains, and cross-chain aggregation capabilities. The tokens supported on the Aave-Evmos DEX include EVMOS, AAVE, USDT, USDC, DAI, wBTC, FRAX, and ATOM.
Celestia partnered with Evmos to create a settlement layer for EVM roll-ups. EVM roll-ups allow users to perform off-chain transactions with minimal transaction fees while transmitting transaction details to the on-chain consensus and information access layer for security. Roll-ups provide developers and consumers with high throughput by executing transactions outside of the Layer 1 chain, reducing congestion.
Cevmos (taken from Celestia/EVMos/CosmOS) is an open source, integrated stack for EVM-based applications that use Celestia roll-up. The Cevmos stack will be based on an enhanced settlement chain, implemented as a Celestia roll-up using the Optimistic Tendermint.
The Settlement chain uses Celestia as an information accessibility layer and Evmos applications (smart contracts, interoperability, aggregation, etc.) to provide a complete EVM equivalent stack for smart contracts interoperable on Cosmos and EV worlds. In contrast to the Ethereum Mainnet, the network is enhanced specifically for roll-ups.
Evmos is leading in cross-chain connectivity between Ethereum and Cosmos. By connecting the two chains, Evmos is helping users avoid the high transaction costs and network bottlenecks that plague Ethereum. Besides, it allows Cosmos developers to exploit the industry leading smart contract network with some limitations.
Ngoài PancakeSwap, hệ sinh thái BNB Chain còn có một AMM khác có TVL đạt 150 triệu USD chỉ sau hai tháng ra mắt, dự án này được gọi là Thena.
Blockade Games provides a platform that allows developers to create blockchain games. In addition, Blockade Games also creates many interesting free games.
UNQ Club is a project that provides a blockchain platform that allows investors to collect and manage existing NFT assets.
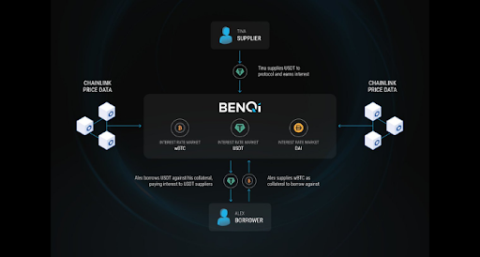
BENQI is one of the important pieces of the Avalanche ecosystem. Join TraderH4 to find out what BENQI (QI) is as well as detailed information about the QI token.
In addition to a cryptocurrency storage wallet, SafePal is also known to many investors for its SFP tokens and airdrop events with attractive rewards.
The fever from Akita Inu in the Crypto market in the past time has created a great buzz along with the rapid development of the "dog house token".
What is IoTeX? This is a blockchain built and developed in conjunction with the Internet of Things (IoT). Join TraderH4 to learn this article.
What is OKB? OKB is an exchange coin of OKX and the OKX Chain blockchain. Let's learn about OKX and OKB exchanges with TraderH4 in this article.
DROPP GG brings an innovative and novel idea to provide an NFT mint platform based on geographies outside of the real world.
CronaSwap is a DEX built on Cronos Chain, which has a similar model to Uniswap.