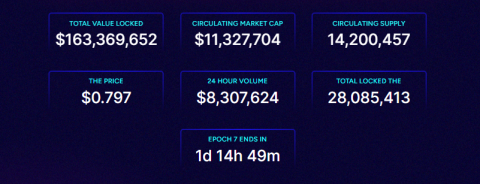
What is Equilibre? Things to know about Equilibre
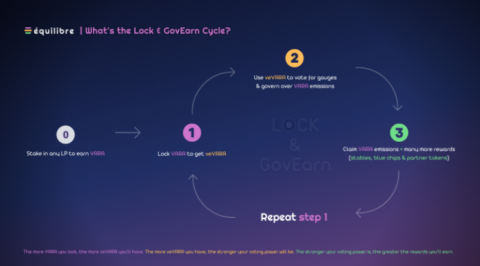
In the framework of this article, let's learn about the Equilibre project with the TraderH4 team - a ve(3,3) AMM of Kava built on the idea of Velodrome.
DeFi is an open space, completely decentralized and fair competition. Projects in the DeFi market must create great value for the community in order to develop sustainably and long-term. AMM is considered as one of the important pieces of the puzzle and is noticed by many project developers. So have you ever wondered how an AMM works? To continue the series of articles on analyzing the operating model of Protocols/DApps, today TraderH4 will analyze the operating model of Uniswap V2 - the giant AMM in the decentralized financial market.
Uniswap is an Automated Market Maker ( AMM ) protocol built on the Ethereum Blockchain that allows users to swap between ERC-20 tokens.
You can find more basic information about Uniswap in Uniswap's on-chain data analysis here .
Uniswap V2 is a step up from Uniswap V1, in V2 you can swap (swap) back and forth between ERC-20 tokens. Uniswap uses a liquidity pool instead of an order book.
Read more: Uniswap 2021 Complete Guide.
Components participating in the model
Liquidity Provider (LP) for short: acts as a supply, providing assets to create liquidity for the market.
User (User/Trader): acting as a demand source, users can trade any ERC-20 tokens on Uniswap and pay 0.3% fee per transaction.
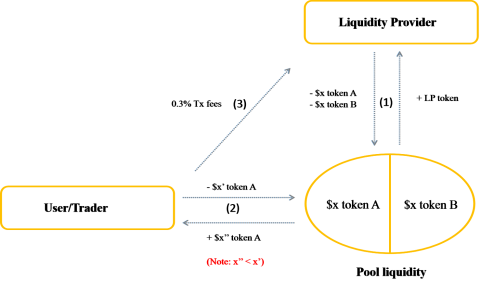
The operation process of the Uniswap model is described in 3 main steps:
Step 1: The liquidity provider (LP) will provide 2 types of assets (A and B) to the respective liquidity pool (A/B) on Uniswap with the ratio 1:1. Then receive the LP token, this token represents ownership of a part of the assets in that pool.
Step 2: Users (User/Trader) who want to swap (swap) token A to token B must put token A into the corresponding pool and receive token B.
Step 3: For each swap transaction, the user has to pay 0.3% transaction fee, this fee will be paid to the liquidity provider (LP).
To make it easier to imagine, I will illustrate in the image below.
Uniswap V2 . Operation Model
Through the model, it can be seen that:
The model does not have any intermediaries, but it is still possible to connect the supply side (LP) and demand side (User/Trader), both of whom share benefits for each other.
To connect supply and demand, Uniswap creates algorithms, programmed according to predefined programs, making all operations run smoothly without the need for a 3rd party. And thereby creating an exchange. Completely decentralized translation.
Read more: What is PancakeSwap and what to know about CAKE token?
The Uniswap algorithm uses
The algorithm on Uniswap is based on the formula: x * y = k.
In there:
Then, the liquidity in the Pool will form a curve as shown below, with the vertical axis being the number of Token B and the horizontal axis being the number of Token A.
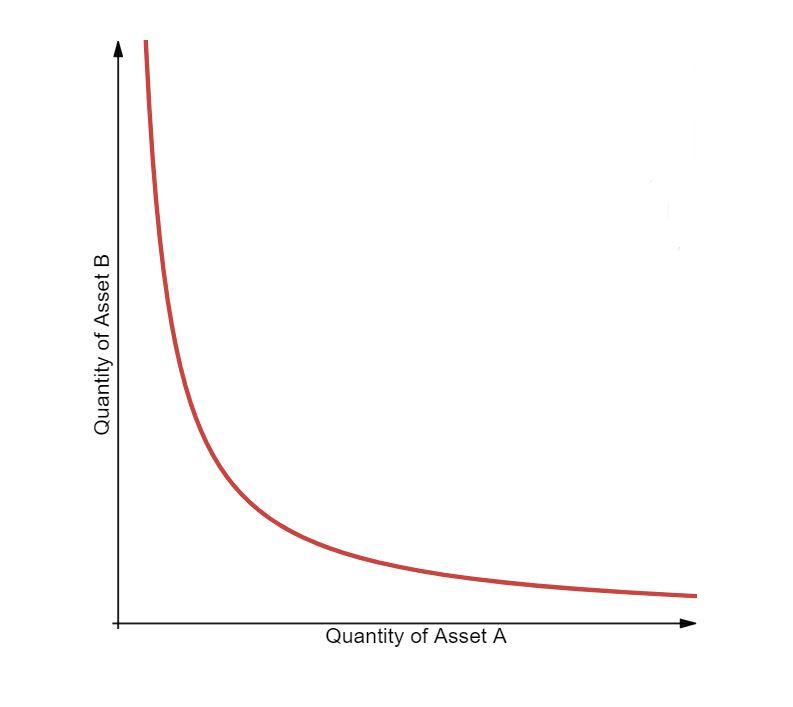
The Uniswap algorithm uses
So what happens when there is a transaction? I will take the ETH/USDT pair as an example for you to easily visualize:
Note: the price in the example I assume is the ideal price, but in fact the price will depend on market fluctuations, you can refer to the prices of cryptocurrencies on Coingecko or Coinmarketcap.
Let's say the pool is created from ETH/USDT pair with 10 ETH and 10,000 USDT for 1 ETH = 1000 USDT and 1 USDT = 0.001 ETH.
Then the total liquidity in the pool: x * y = k ⇔ 10 * 10,000 = 100,000.
I will join this pool swap 5,000 USDT and pay 0.3% fee in exchange for ETH.
=> y' = 5,000 + 10,000 = 15,000 USDT
With k = 100,000 unchanged.
=> x' = 6.66 ETH,
So I will receive the amount of ETH = x - x' = 10 - 6.66 = 3.33, with a value equivalent to 5,000 USDT => 1 ETH = 1,500 USDT, an increase of 50% compared to the original value.
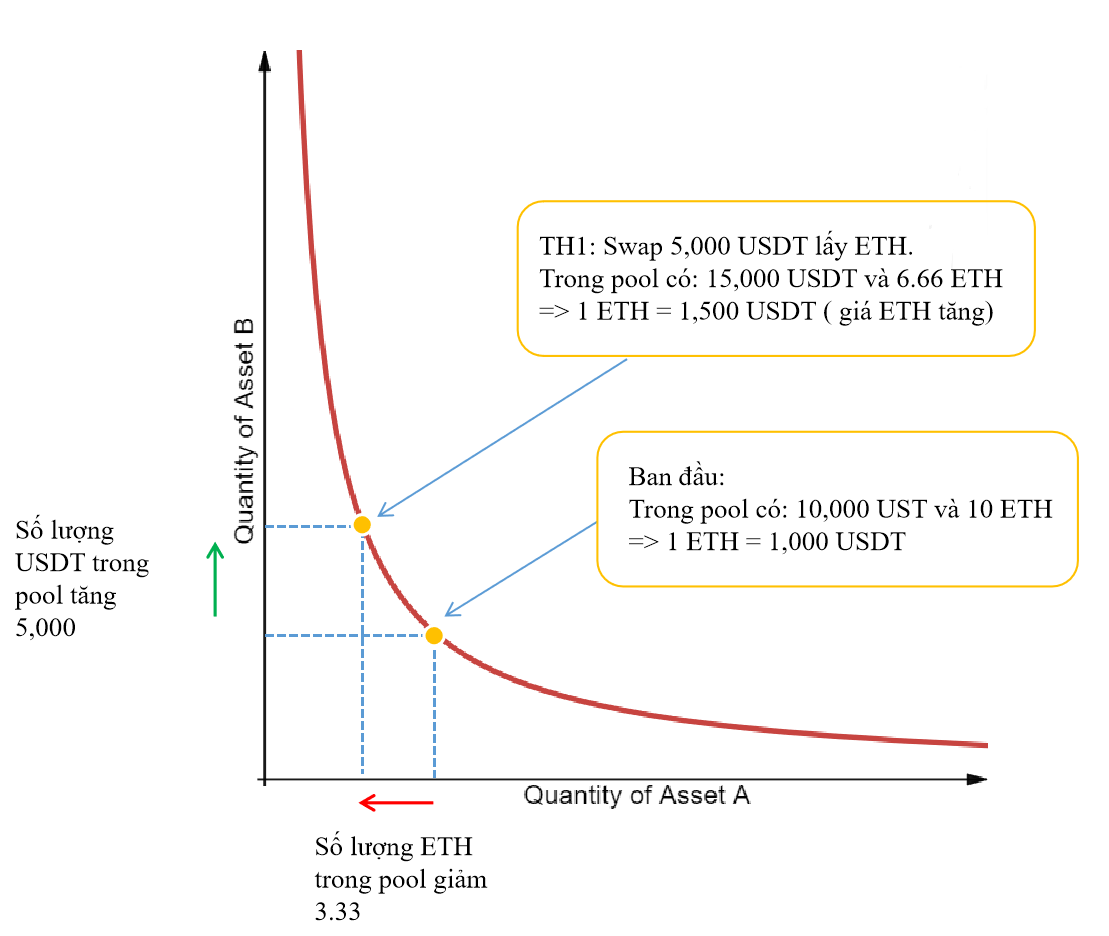
Swap USDT for ETH
Why is the price of ETH rising?
It can be understood simply that I increased the USDT part and decreased the ETH part of the group, so the reason the ETH price increased is because the amount of ETH in the Pool after I made the Swap has decreased but the total liquidity (k) is always 1 constant, thus causing the price of ETH to increase compared to the original.
Note: 0.3% fee will be added back to the pool after the swap changes the value of k.
I will go to this pool to swap 6 ETH for USDT.
=> x' = 10 + 6 = 16 ETH,
With k = 100,000 unchanged.
=> y' = 6250 USDT
So I will receive the amount of USDT = y - y' = 10,000 - 6,250 = 3,750 with the equivalent value of 6 ETH => 1 ETH = 625 USDT, 37.5% down from the original value.
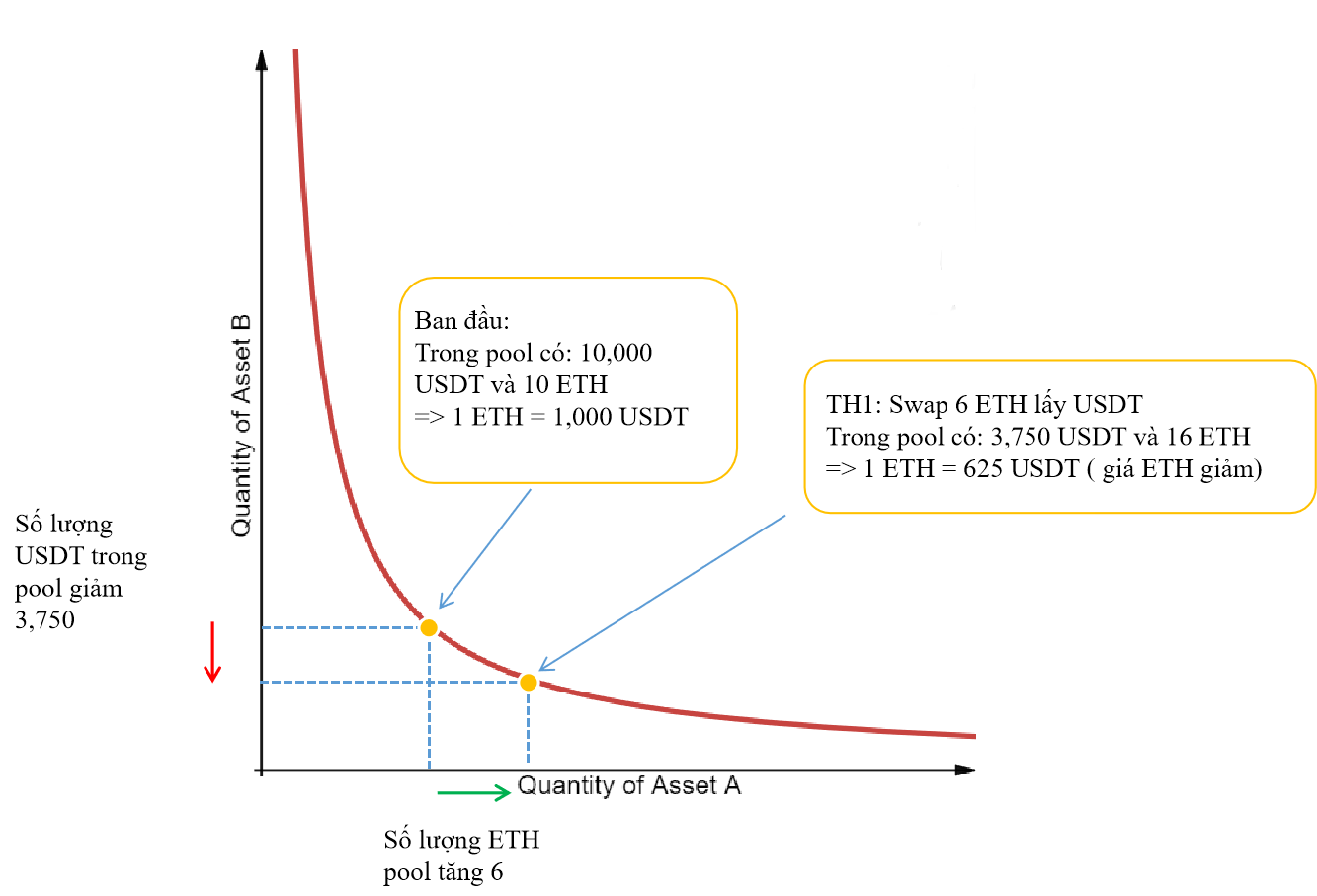
Swap ETH for USDTB
At this point, you can explain why the price of ETH has dropped, right?
Note: in fact, the larger the volume of transactions, the more different the equilibrium ratio between x and y, i.e. cannot change linearly. When the trading volume is high, the price of the cryptocurrency in the pool will be exponentially more expensive than trading with a small volume if the liquidity in the pool is not enough (this is called slippage). So to reduce slippage and contribute to faster processing of high volume transactions requires large liquidity in the pool. Therefore, you need to consider the liquidity in the pool before making a trade.
Read more: What is Ethereum 2.0 and why is Ethereum 2.0 important?
Pool model on Uniswap
Uniswap uses a pool model with a 50:50 ratio, most pools in Uniswap will be made up of 50% ETH and 50% ERC-20 tokens.
ETH is used as a common currency on Uniswap and helps to connect pools together. For example, if you own token A and want to swap with any other token on Uniswap (eg token B), your swap will go like this: Token A => ETH => Token B.
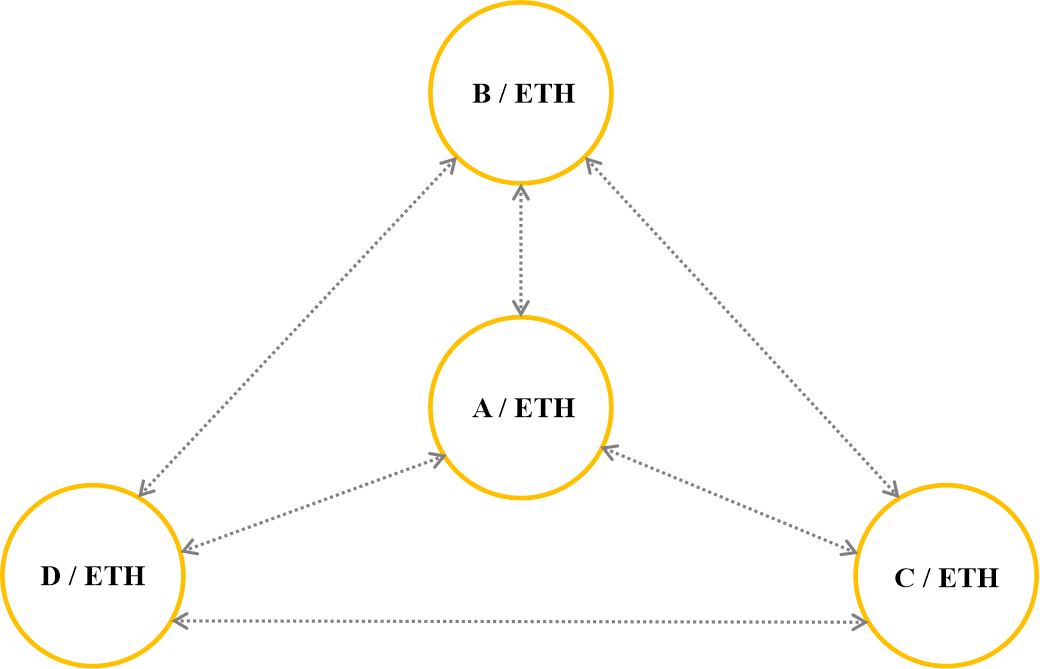
Pool model on Uniswap

Pool model on Uniswap
Uniswap created a great decentralized exchange and is completely non-profit when 100% of the transaction costs on the exchange will be paid to the liquidity provider for the pool. However, for Uniswap V2 encountered 2 main problems:
Firstly, transaction fees on ETH are quite high, which hinders Uniswap's access to other small investors. With this issue, I expect to be resolved in Uniswap V3. TraderH4 will soon have an article about the working model of Uniswap V3. Let's look forward to it!
Read more: Uniswap v3 launch helps DeFi thrive during last week's downturn.
Second, liquidity providers face temporary losses.
Suppose: I deposit 1 ETH and 1000 USDT (ratio 1:1, for 1 ETH = 1000 USDT) to a respective pool on Uniswap. On the pool there are 10 ETH, 10,000 USDT and the total liquidity (k) in this case is 100,000. So I have 10% stake in this case. So I face temporary loss if ETH rises to 4000 USDT this changes ETH and USDT price ratio in the pool. As a result, users will add more USDT to the pool and withdraw ETH from it until this ratio reflects the correct price (total liquidity k remains constant), so now there will be 5 ETH in the pool and 20,000 USDT. So I withdraw and will receive 10% of the total amount of 0.5 ETH and 2,000 USDT with a value of 4000 USDT. I had a profit of 2,000 USDT but if I don't deposit it in the pool, my profit is 3,000 USDT (1 ETH and 1,000 USDT, 1 ETH = 4,000 USDT).
Note that this effect occurs even when the price falls from the time it was deposited into the pool. As for you keeping ETH in your wallet, if the ETH price drops, the loss can be huge compared to sending ETH to the pool, because when you deposit ETH into the pool, you will receive the user's transaction fee when making a transaction. on Uniswap.
This problem is an unavoidable risk so the liquidity provider must consider when deciding to deposit cryptocurrencies into the pool.
Read more: Ampleforth On-chain Data Analysis (AMPL) – What is the demand for Algorithmic Stablecoins?
Above is useful information about Uniswap V2's operating model from many sources that TraderH4 synthesizes and researches for readers. Hope to help you better understand the project and operating model of an AMM, which is currently leading in the DeFi market.
According to readers, is Uniswap V2's operating model really effective? Discuss with us at Telegram Group TraderH4. And don't forget to visit TraderH4's website to quickly update the upcoming events of the project. See you again in the next issue of "Active Model Analysis" of TraderH4.
Note: All information in this article is intended to provide readers with the latest information in the market and should not be considered investment advice. We hope you read the above information carefully before making an investment decision.
In the framework of this article, let's learn about the Equilibre project with the TraderH4 team - a ve(3,3) AMM of Kava built on the idea of Velodrome.
Gamma Straregics provides a solution to the problem of concentrated liquidity in a certain price range. Let's learn about this project with TraderH4 in the article below.
Ngoài PancakeSwap, hệ sinh thái BNB Chain còn có một AMM khác có TVL đạt 150 triệu USD chỉ sau hai tháng ra mắt, dự án này được gọi là Thena.
Blockade Games provides a platform that allows developers to create blockchain games. In addition, Blockade Games also creates many interesting free games.
UNQ Club is a project that provides a blockchain platform that allows investors to collect and manage existing NFT assets.
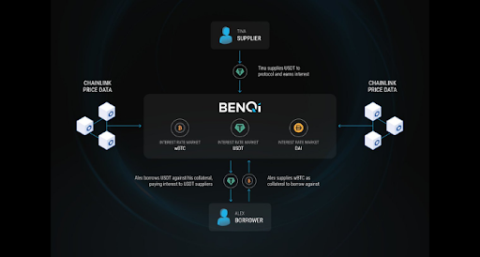
BENQI is one of the important pieces of the Avalanche ecosystem. Join TraderH4 to find out what BENQI (QI) is as well as detailed information about the QI token.
In addition to a cryptocurrency storage wallet, SafePal is also known to many investors for its SFP tokens and airdrop events with attractive rewards.
The fever from Akita Inu in the Crypto market in the past time has created a great buzz along with the rapid development of the "dog house token".
What is IoTeX? This is a blockchain built and developed in conjunction with the Internet of Things (IoT). Join TraderH4 to learn this article.
What is OKB? OKB is an exchange coin of OKX and the OKX Chain blockchain. Let's learn about OKX and OKB exchanges with TraderH4 in this article.
DROPP GG brings an innovative and novel idea to provide an NFT mint platform based on geographies outside of the real world.
CronaSwap is a DEX built on Cronos Chain, which has a similar model to Uniswap.