What is thena? Discover the outstanding features of Thena and THE . token
Ngoài PancakeSwap, hệ sinh thái BNB Chain còn có một AMM khác có TVL đạt 150 triệu USD chỉ sau hai tháng ra mắt, dự án này được gọi là Thena.
Interoperability is becoming an increasingly important part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As more and more Layer 1 and Layer 2 become specialized, some values become blurred, which solves one problem but creates another.
These ecosystems are not interoperable by default. They create a set of isolated environments, but all the chains and applications built on top need to communicate with each other to reach their full potential. This problem has sparked a new wave of bridging solutions with the goal of connecting ecosystems together.
The most common design approach for bridged chains involves the use of specialized chains as bridges, also known as middlechains, such as Wormhole or Ronin. These intermediaries connect two blockchains by establishing two-way communication between them on a one-to-one basis (e.g. Ethereum with Solana). But this approach is limited. Adding a new chain to the network becomes exponentially harder for each added chain. Router Protocol has taken an innovative approach to avoid the added complexity and cost of this process.
Instead of performing a one-to-one bridge for every connection, the Router generalizes the process of plugging in new chains. The protocol adopts a mesh network architecture where chains are pluggable and instantly connected to other participating chains.
Router was founded in August 2020 by Ramani Ramachandran, Shubham Singh, Chandan Choudhury and Priyeshu Garg. Following the advent of many new Layer 1 projects and scaling solutions, the project development team recognized the need for a better interoperability infrastructure. Traditional bridging solutions are too slow and only focus on connecting two ecosystems.
The project raised an initial seed round of $485,000 and in October 2021 raised an additional $4.1 million from investors including Polygon and Coinbase Ventures.
Router Protocol is an extensible cross-chain bridge, built as a network of chains and connected through a series of nodes. These nodes have bridge contracts deployed on each chain connected to the network. Bridge contracts can listen and execute transactions to facilitate the transfer of value between chains. The transfer of value can happen in a number of ways such as locking assets in the source chain and unlocking or mining assets in the destination chain. The protocol can also be used to forward data between chains, to perform cross-chain actions without connecting assets.
The router currently connects nine EVM-based chains including Ethereum, Polygon, BNB Chain, Avalanche, Fantom, Arbitrum, Cronos, Harmony, and Optimism. The project development team is currently working on adding Aurora and Moonbeam to the network. Besides that, they are also working to integrate non-EVM chains like Solana, Algorand and the Cosmos ecosystem into the network. Their first step will be the Cosmos ecosystem through building on the CosmWasm module.
With the first phase, the Router is currently in limited production. In this release, the team controls three system security nodes. However, the team is working to migrate the protocol to a standalone, base layer blockchain network built using the Cosmos SDK.
Voyager: Swap any token
Router Voyage Dapp gives users the ability to swap any token on the source chain for any token on the destination chain.
There are seven scenarios in which a handover can take place with the Router Protocol, and the associated assets can fall into three categories. The three types of assets are:
Here are some examples of transmission scenarios that can be executed via Router Protocol.
Stable-to-Stable Reserve Asset Transfer
Consider a user who wants to transfer USDC from chain A to chain B.
This is the simplest case. In this case, a stablecoin like USDC would be locked in the source chain and unlocked on the destination chain. However, if there is not enough liquidity on the destination chain, the user receives a reserve version of the asset, in this case RUSDC.
Stable-to-Non-Stable Reserve Asset Transfer
Consider a user who wants to transfer USDC from chain A to MATIC on chain B. There are two possible transfers:
In this case, USDC is locked on the source chain and then unlocked on the destination chain. The unlocked USDC will then be swapped for MATIC.
Liquidity conditions vary on-chain so this route may not always be feasible. This brings us to the second route.
The router will swap USDC for MATIC on the source chain and lock it and unlock MATIC on the destination chain.
Arbitrary Asset to Mintable Asset Transfer
Consider a user who has an APE on thread A and wants to swap it for ROUTE on thread B.
Here, the Router will swap the APE for ROUTE, lock it on the source chain, and generate an equal amount of ROUTE on the destination chain.
Arbitrary Asset to Arbitrary Asset Transfer
Consider a user who wants to swap AAVE from thread A for JOE on thread B.
The router will swap AAVE for USDC on the source chain and lock it. It will then unlock the USDC and swap it for JOE on the destination chain.
The router gives users several options when it comes to paying transaction fees. Users can pay with native tokens on the source chain (e.g. pay fees in ETH if on the Ethereum network). They can also pay with USDC, but users who pay transaction fees with ROUTE or DFYN will get 50% and 20% discount respectively. For example if the transaction fee is 4 USD in USDC, it will cost 2 USD in ROUTE. This discount amount is subject to change in the future.
Router implements a proprietary pathfinding algorithm that runs off-chain with the aim of finding the most efficient route to transfer values between chains.
Depending on the type of transfer, the Pathfinder algorithm will run different scenarios to determine which "route" is the most optimal. These routes can be chosen between using their own liquidity pools to facilitate transfers, leveraging a Dfyn DEX partner, or evaluating on a third-party DEX on one or both two chains.
The ultimate goal of projects like Router is not merely to act as a bridge but also as a developer's platform. These platforms will allow developers to unlock new use cases that are only possible through the simultaneous interaction of multiple chains. These developer platforms will be the new layers on which applications can be built and abstract away the complex interactions that take place in the background from the end user. With that in mind, Router has been developing a customizable SDK and widget so developers can build cross-chain apps that leverage Router Protocol.
ROUTE is a utility/administrative token for Router Protocol. This is an Ethereum-based ERC-20 token with a maximum supply of 20,000,000.
ROUTE launched on January 16, 2021 has been listed directly on AscendEx. The ROUTE token can also be found on DEXs like Uniswap and centralized exchanges like KuCoin.
ROUTE can be used for four main purposes, which are:
Administration
ROUTE token holders can participate in the governance of the project by voting on proposals regarding modifications and upgrades of the protocol on Snapshot. These include issues like establishing a liquidity mining length or which new chains to add to the network.
Revenue sharing
Router Protocol revenue is generated from transaction fees distributed between validators and liquidity providers.
Minimize transaction fees
The router offers users the ability to pay transaction fees in several ways, but users who pay transaction fees with ROUTE or DFYN will now receive 50% and 20% discounts, respectively.
The router launched its initial swap between Polygon and BNB Chain in January 2022. In March 2022, they followed up with the addition of Avalanche and then Fantom and Ethereum. The router currently supports a total of nine chains.
Overall, the cumulative volume on the network exceeds $215 million, with over 25,000 transactions. The Polygon-Fantom connection is currently the most traded route, with a volume of over US$200 million. The Polygon-Arbitrum connection has also recently seen an increase in activity, reaching over $2.25 million in volume and acquiring over 2500 new users, with most of the volume accumulating since the announcement of the campaign. Incentive bridging on June 21.
While it is difficult to distinguish (in transactional data) between human and bot activity, overall activity in the protocol has increased significantly around the three Router incentivized bridging competitions. Looking at the total USD remittance value of addresses across the user base shows the extent of the volume contributed by individuals within the user base. The top 5 addresses account for over 14,000 total transactions and most of the overall volume.
Non-EVM chain integration in Q2 & Q3 2022
The router has targeted more than just EVM chaining. The project wants to connect every chain that can support a bridge contract. The list starts with strings like Solana, Algorand, and Terra. The difficulty of connecting these chains will vary from chain to chain, but the Router team has made significant progress in implementing the first Non-EVM bridge contract through the CosmWasm module.
Launching Router CrossTalk Library in Q2 & Q3 2022
Recently, the team launched their cross-chain SDK called CrossTalk. It allows forwarding of common messages and transitioning state between different chains, allowing developers to build native cross-chain applications. The framework has previously undergone three security checks from Certik and Halborn and Hacken and is currently performing additional testing procedures. However, developers can now start building on the dev environment.
Re-launching Router V2 on dedicated chain Q4 2022 to Q1 2023
The router is expected to move to its own dedicated blockchain, built using the Cosmos SDK. Acting as an application-specific thread has several benefits. Specifically, the router will be able to maintain an on-chain account of all actions performed by the protocol as well as enhance interoperability through the governance framework of IBC and Cosmos.
While the high-level architecture will remain the same, the current validation mechanism will move from a set of Router nodes running on top of a GoLang instance to its own Cosmos Hub chain with Tendermint consensus-based authentication .
Routers compete in a diverse market with several solutions that facilitate monthly transfers of billions of dollars. However, this is a nascent market and is unlikely to see winner-take-all dynamics like the AMM space.
In contrast to the DEX sector, where Uniswap dominates around 77% of the market, the market for interoperability infrastructure players is likely to be more evenly distributed. Interoperability solutions have a larger design space, in contrast to the AMM model, which is difficult to improve. Several projects were quickly adopted due to their unique solutions: WRAPPED features content-specific bridging; THORChain focuses on native asset swaps, and Synapse leverages its own multi-liquid pools. The success of different projects demonstrates the high demand for bridging solutions with different focuses.
Security continues to be a major factor in the interactive space, as there have been many well-documented cases of bridges being hacked, most recently with Ronin. The router has taken various measures such as performing various tests and launching a bug bounty program in conjunction with Immunefi.
The router has implemented a dedicated proxy architecture that allows for contract upgrades in the event of a vulnerability or failure. The protocol also has an isolated execution pallet that allows tamper-proof function calls.
Countless chains are now apparently active, being at a different stage in terms of the number of assets, applications built on top, and corresponding liquidity. There are also cases where there are different virtual stacks, e.g. EVM/Non EVM. Because of these differences, the conditions for cross-chain operations, in particular the transfer of value between them, will vary depending on the source and destination chain combinations. For this reason, a competitive bridging solution would need to be highly modular in terms of its functionality.
A protocol like Router can solve these problems. It can make best use of comparable bridging solution approaches such as cross-chain data transfer to perform cross-chain actions. Router Protocol can also take advantage of its own multiline liquidity pools. The project offers the ability to transfer native assets as well as plug into any available DEX and package them into a single solution.
So far, the Router has successfully connected nine EVM chains. The project also offers Voyager, which provides an intuitive DEX-like UX with the added functionality of selecting the source and destination of the content. However, routers still face the biggest challenge of capturing a significant portion of the cross-chain infrastructure market. Include:
Routers have set out to address these challenges by finalizing their first plan to host their own Tendermint-based chain. Once deployed, the Router will be able to fully decentralize validation. The project team is also adding support for non-EVM-based chains, starting with Cosmos through CosmWasm, followed by Solana and Algorand.
Router also just released CrossTalk, a cross-chain communication framework for developers to build native cross-chain applications. CrossTalk will help Router build the foundation as a chain agnostic development platform. Ultimately, if the router successfully implements the aforementioned solutions, it may find itself in a unique position to capture users and market share.
Ngoài PancakeSwap, hệ sinh thái BNB Chain còn có một AMM khác có TVL đạt 150 triệu USD chỉ sau hai tháng ra mắt, dự án này được gọi là Thena.
Blockade Games provides a platform that allows developers to create blockchain games. In addition, Blockade Games also creates many interesting free games.
UNQ Club is a project that provides a blockchain platform that allows investors to collect and manage existing NFT assets.
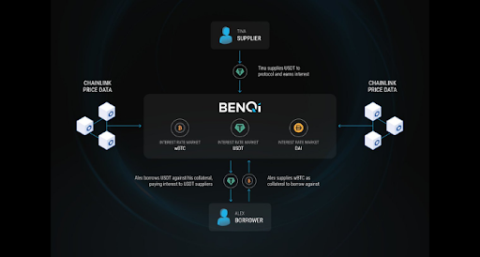
BENQI is one of the important pieces of the Avalanche ecosystem. Join TraderH4 to find out what BENQI (QI) is as well as detailed information about the QI token.
In addition to a cryptocurrency storage wallet, SafePal is also known to many investors for its SFP tokens and airdrop events with attractive rewards.
The fever from Akita Inu in the Crypto market in the past time has created a great buzz along with the rapid development of the "dog house token".
What is IoTeX? This is a blockchain built and developed in conjunction with the Internet of Things (IoT). Join TraderH4 to learn this article.
What is OKB? OKB is an exchange coin of OKX and the OKX Chain blockchain. Let's learn about OKX and OKB exchanges with TraderH4 in this article.
DROPP GG brings an innovative and novel idea to provide an NFT mint platform based on geographies outside of the real world.
CronaSwap is a DEX built on Cronos Chain, which has a similar model to Uniswap.