Analysis of SushiSwap operating model – Multi-product model
Today TraderH4 will analyze the operating model of SushiSwap - an AMM that integrates various business models in the decentralized financial market.
First, if you don't know how Unswap V2 works? TraderH4 invites you to read the Uniswap V2 operating model analysis here, to better understand the basic operating mechanism of an AMM in general and Uniswap V2 in particular. Then come back and read this article.
Uniswap V3 is the latest update of Uniswap and hit Mainnet on June 5, 2021. The goal of this upgrade is to maximize capital efficiency with new changes such as:
Centralized liquidity provision: allows liquidity providers (LPs) to set custom price ranges for the liquidity of the LP offering. That is, liquidity will be concentrated in a price range in which the majority of trades take place.
Multiple transaction fees: LPs will receive profits in accordance with their liquidity contribution to accept different levels of risk.
Uniswap LP token as NFT: each LP position on Uniswap is unique because each user who deposits tokens into the pool can self-adjust the price range. Therefore, each LP position is represented by an NFT.
Read more: Tutorial on how to create your own NFT.
These changes have made Uniswap V3 a flexible AMM that offers users benefits such as:
Maximize profits for liquidity providers: up to 4000x capital efficiency compared to Uniswap V2.
Reduce the risk of providing liquidity to the pool and grow more Pools.
Reduce slippage when trading large amounts of cryptocurrencies.
Range orders: Allows placing limit orders, profit taking orders on Uniswap.
Read more: Uniswap 2021 Complete Guide.
Components participating in the model
Still like Unswap V2, the parties involved in the model include:
Liquidity Providers (LPs for short): act as a supply, providing assets to create liquidity for the market.
User (User/Trader): acting as a demand source, users can trade any ERC-20 tokens on Uniswap.
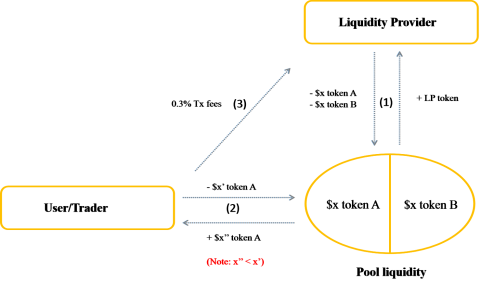
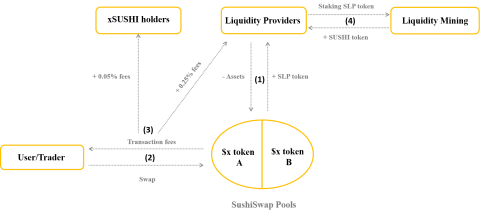
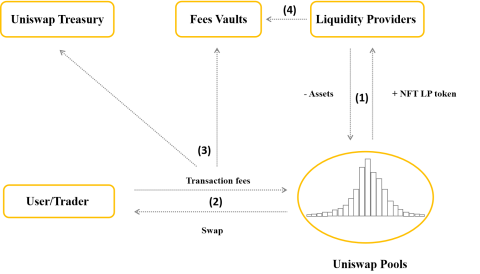
The operation process of Uniswap model is described in 4 main steps:
Step 1: Liquidity providers (LPs) will provide assets to a centralized liquidity pool on Uniswap. Then receive NFT LP token, this token represents ownership of part of the assets in the pool.
Step 2: Users (User/Trader) who want to swap (swap) in Uniswap Pools must pay the transaction fee for the protocol (Protocol).
Step 3: The transaction fee consists of 2 parts: 10-25% of the transaction fee will be sent to Uniswap Treasury, the rest will be taken to Fees Vaults.
Step 4: Liquidity providers will receive fees from Fees Vaults.
Read more: Uniswap v3 launch helps DeFi thrive during last week's downturn.
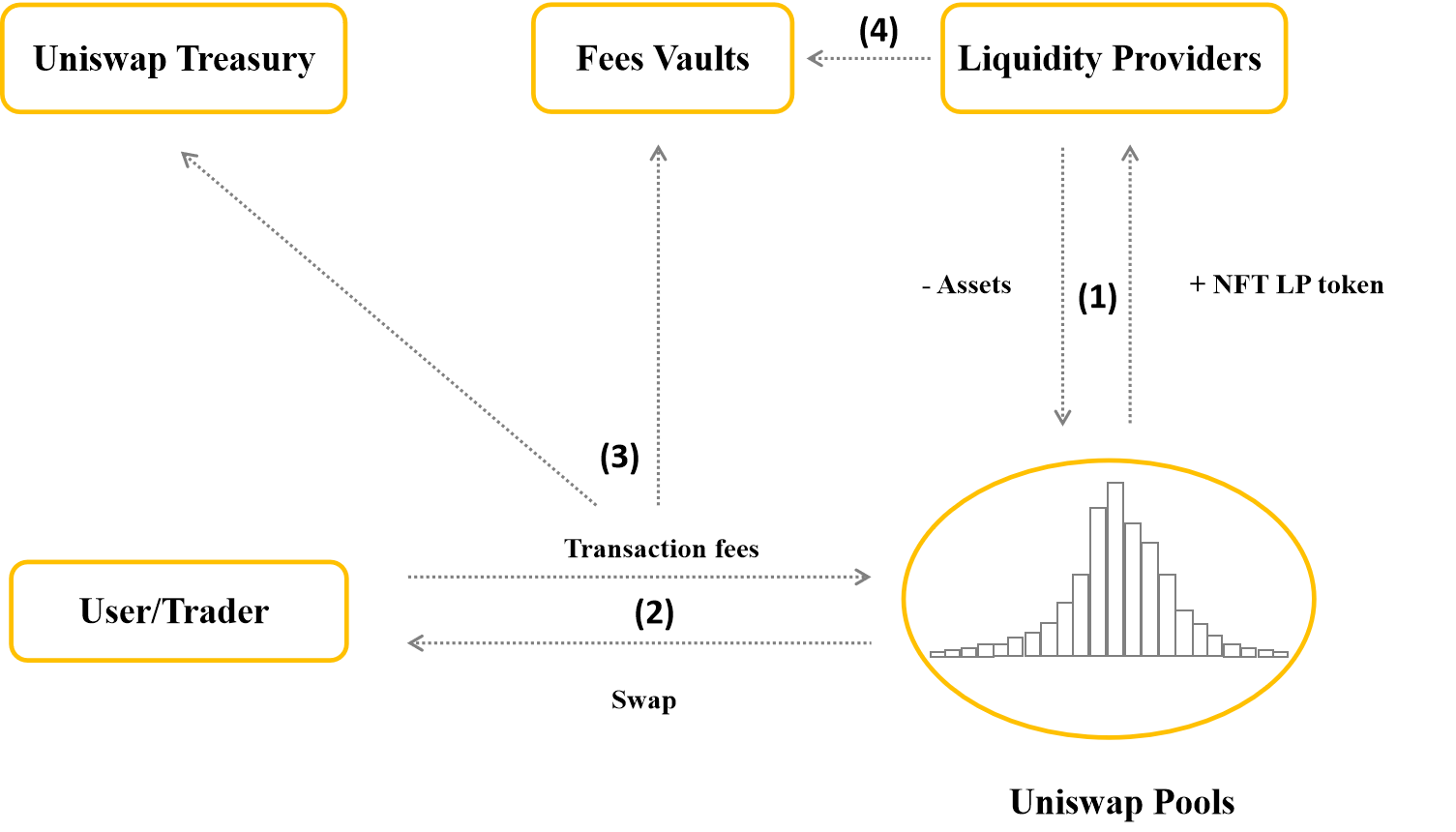
Uniswap V3 . Operation Model
Read more: What is PancakeSwap and what to know about CAKE token?
The change in infrastructure of Uniswap V3
The operating model in Uniswap V3 appeared many new components such as: NFT LP token, Uniswap Treasury, Fees Vault, etc. However, the change in infrastructure of Uniswap V3 is the weapon that affects the operating model. Uniswap V3.
Provide centralized liquidity in Uniswap V3.
In the Uniswap V2 model, the liquidity in the Pool follows the x * y = k curve model. That is, the liquidity in the pool will run from 0 to infinity, users can trade at any price with any volume.
But in reality, the price only runs within a certain range. For example, the DAI/USDC pair, the price of this pair only runs between 0.99 – 1.01. So to solve this problem, Uniswap V3 created centralized liquidity feature. That is, instead of providing liquidity from 0 to infinity like uniswap V2. Then in Unswap V3, LPs will provide a range from 0.99 to 1.01. For easy visualization, please see the illustration below.
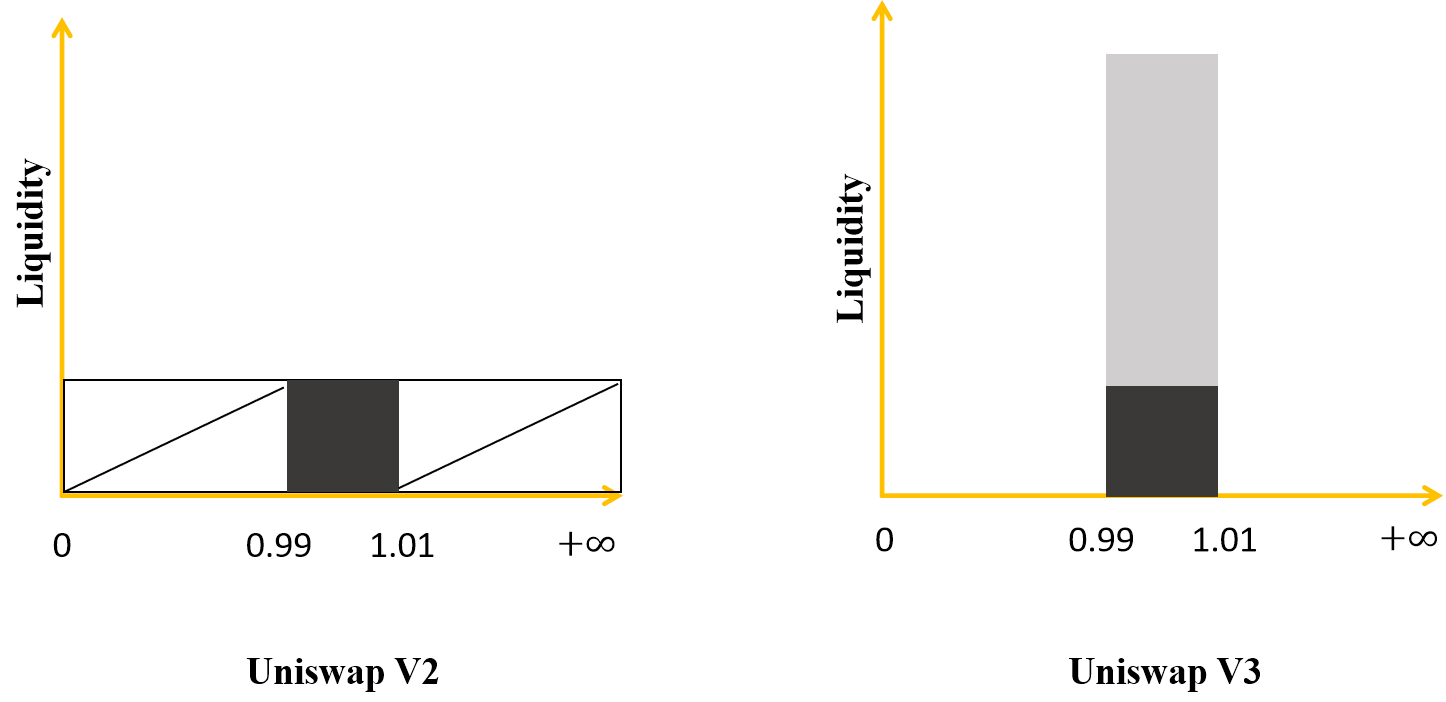
Provide centralized liquidity in Uniswap V3
Read more: Uniswap (UNI) on-chain analysis launches Uniswap V3 what data reveal?
How centralized liquidity works
In Uniswap v3, LPs can centralize their capital within a custom price range, providing a large amount of liquidity at the price the LP desires. In doing so, the LPs will build their own custom curves.
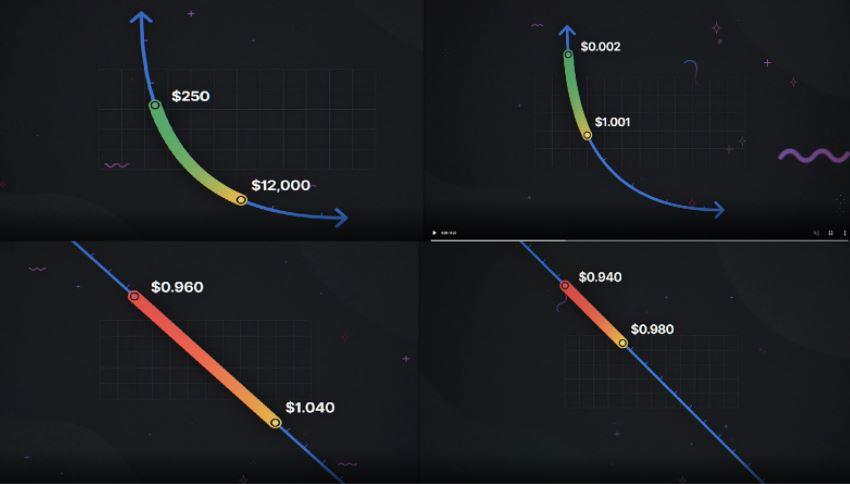
How centralized liquidity works
LPs can concentrate liquidity in a custom price range. For example, an LP in the ETH/DAI pool might choose to allocate $100 for prices between $1,000 and $2,000 and add $50 between $1,500 and $1,750. This way, the liquidity provider can visualize how the market maker or order book is performing.
User (User/Trader) trades based on liquidity aggregated from all individual curves. Trading fees collected at a certain price range will be divided by LPs in proportion to their liquidity contribution within that price range.
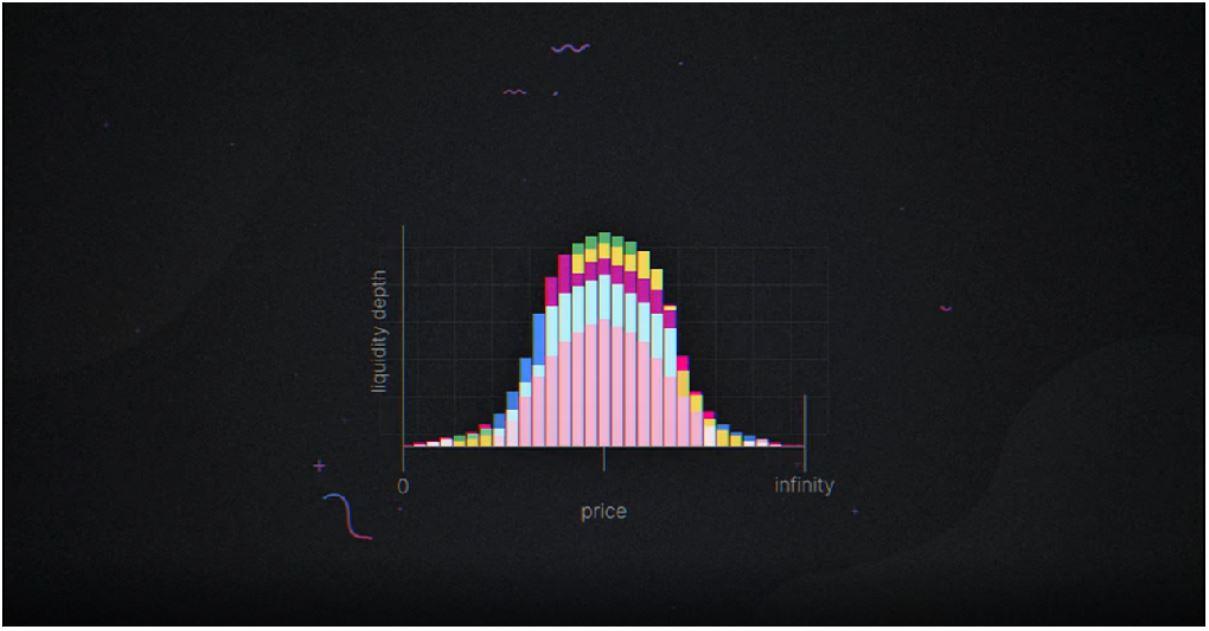
Aggregated liquidity
Conversely, if the market price moves outside the valuation range of an LP then this trade does not use the liquidity this LP provides and will not receive a transaction fee.

Active liquidity
How effective is the use of capital?
Liquidity providers can generate the same level of liquidity as Uniswap V2 within a specific price range but using less capital.
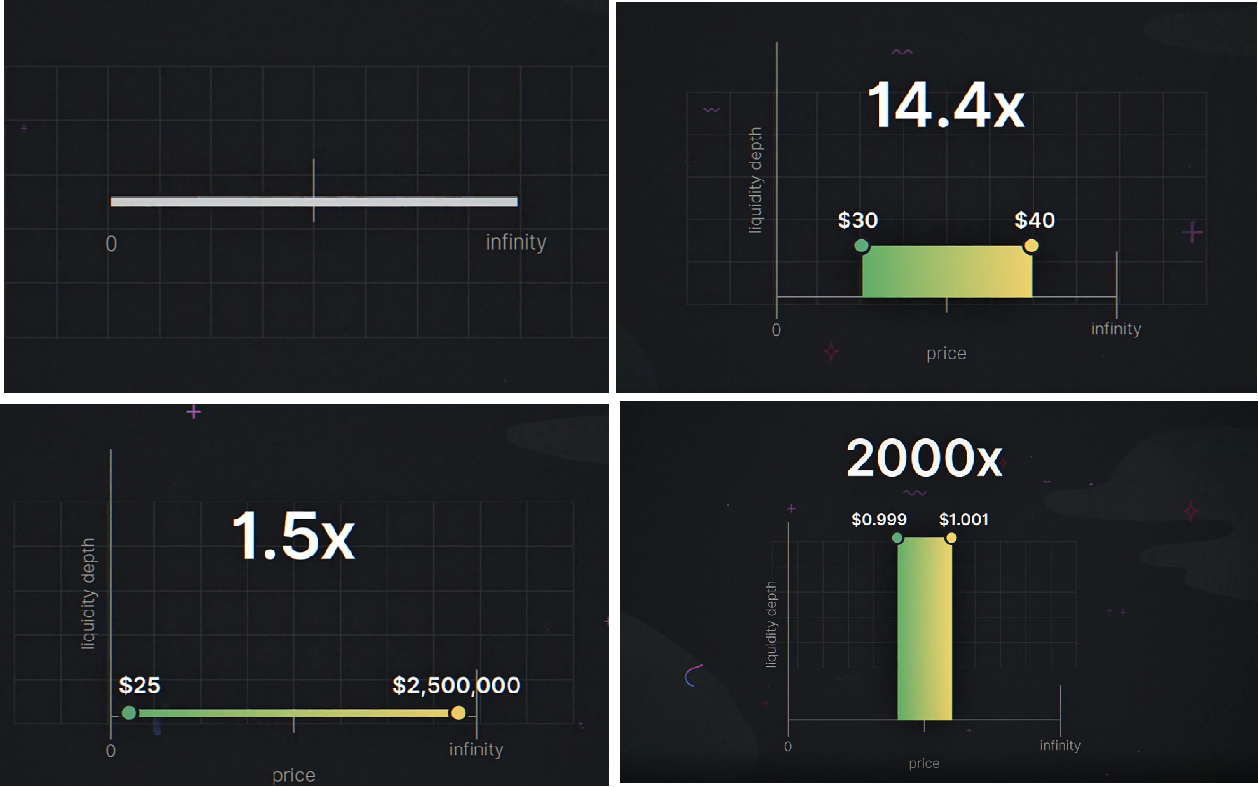
Effective use of capital
To illustrate, I will give Uniswap's own example:
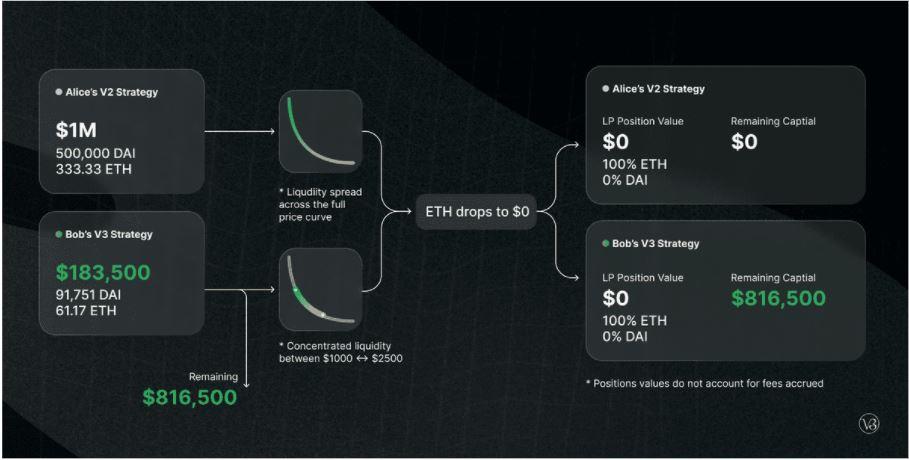
Alice and Bob each have $1M, both want to provide liquidity in the ETH/DAI pool on Uniswap V3. ETH price is 1,500 DAI.
Alice decided to deploy capital on all price ranges (0 – infinity, like the way of providing liquidity on Uniswap V2), in total Alice deposited 500,000 DAI and 333.33 ETH (worth $1M).
Bob only deposits in the $1,000 to $2,250 price range to create a concentrated liquidity position. Bob deposited 91,751 DAI and 61.17 ETH worth a total of about $183,500 and kept $816,500 to invest elsewhere.
The amount Bob spends is less than half of Alice's, but the liquidity Bob provides is equivalent.
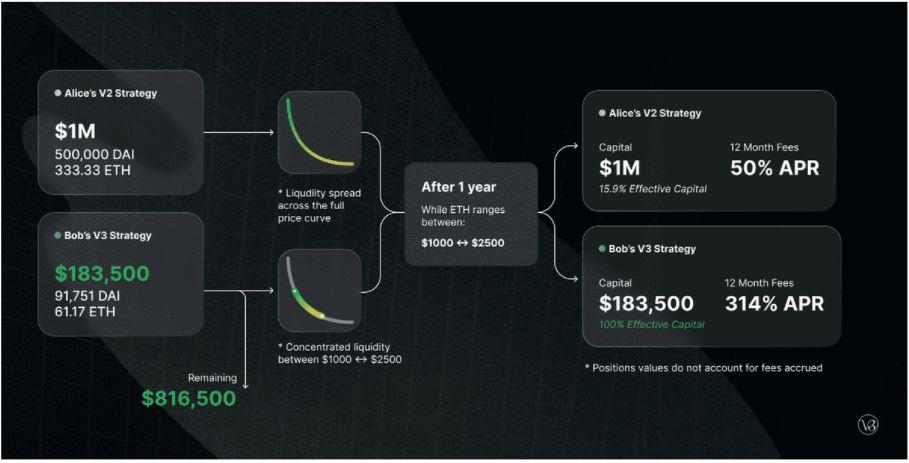
Effective use of capital
Read more: What is Ethereum? The most detailed guide to virtual currency ETH.
Minimize risk when providing liquidity
Suppose the price of ETH drops to $0, in this case 100% of Alice and Bob's LP tokens will be equal to ETH's price of $0.
Result: Bob lost only $183,500 and Alice lost all of her capital.
Minimize risk when providing liquidity
Instead liquidity providers (LPs) in V3 provide the same liquidity as LPs in V2 with less capital. V3 LPs can provide higher liquidity with the same capital as V2 LPs to support larger trades and get higher returns. However, in return V3 LPs suffer a higher temporary loss.
Uniswap's Range order feature
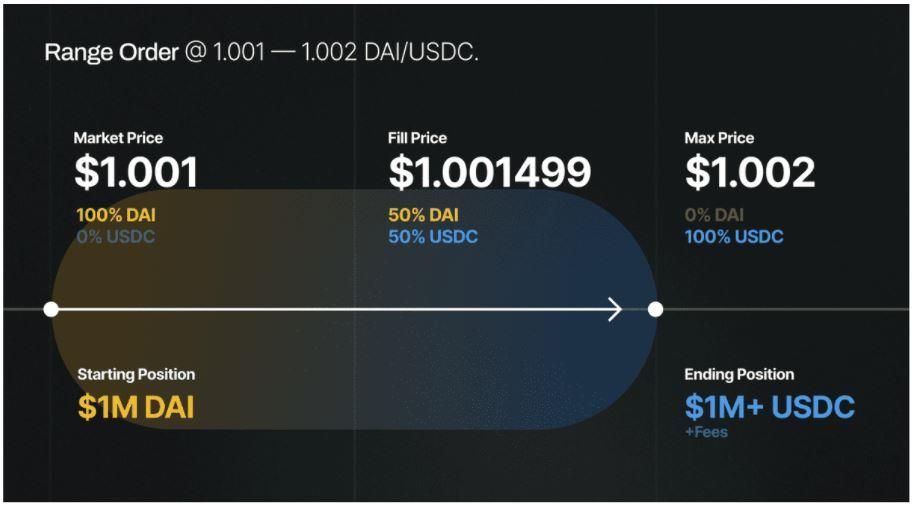
Customization of LPs on Uniswap V3 opens up a new feature called “Range Order – order price range that provides liquidity of LPs”.
This is a feature that allows LPs to provide liquidity of 1 token in a custom price range above or below the market price: if the market price is within this range, the LPs will profit and automatically place orders. Sell limit (Limit Order) 1 token at this price range.
For example:
If the current price of DAI is below 1.001 USDC, I can offer $1M DAI in the zone of 1.001 – 1,002 DAI / USDC.
When DAI trades above $1,002 DAI/USDC, all of its liquidity will convert to USDC. Then the DAI price at trading is equal to the average price of the liquidity segment of $1.0015 DAI/USDC and receives additional trading fees during the period when the trading price is in the range of $1.001 – $1,002 DAI/USDC.
Note: to complete the above process, I have to withdraw my liquidity to avoid automatic conversion of DAI bar if DAI/USDC trades below 1.002.
Uniswap's Range order feature
In the event that DAI fails to go above $1,002, and the price is in the range of $1.001 – $1,002, my order will be partially executed and I will still receive the transaction fee in that part.
Thereby, it can be seen that the Range Order feature allows LPs to profit from transaction fees and from many other investment strategies.
Change the mechanism of transaction fees
In Uniswap V2, transaction fees are 100% paid to liquidity providers. In Uniswap V3 will change more complex as follows:
Firstly, there are many transaction fees, specifically 3 fees are 0.05%, 0.3%, 1%:
Second, Uniswap has started charging transaction fees, which means that 100% of transaction fees are no longer LPs, specifically: 10%-25% of LPs' revenue.
Third, the liquidity that LP provides will be segmented. Therefore, there will be transaction costs based on the proportion of LP tokens that provide liquidity to the extent that the market price trades on that segment.
Fourth, the transaction fee will go to Fees Vault instead of going to Pools like on Uniswap V2, because LP token in Uniswap V3 is NFT, so LP will receive fee at Fees Vault.
Overall, Uniswap V3's operating model is not much different from Uniswap V2's operating model. However, the big changes coming from within the model are changes in the infrastructure and technology of the project. The special thing is that this technology has a 2-year copyright. So the technologies that Uniswap uses for V3 will be unique.
Read more: What is Ethereum 2.0 and why is Ethereum 2.0 important?
With new technologies Uniswap has solved the problem of transaction fees and slippage when making high-volume trades while creating a centralized liquidity supply model. However, there are many other problems that can be mentioned such as:
Firstly, the work of providers becomes more complicated: no longer simply deposit money into pools to provide liquidity and get 100% transaction fees back like in Uniswap V2. Providing concentrated liquidity, opening up more investment opportunities with high returns for LPs, in return requires LPs to have a lot of knowledge to be able to make their own investment strategies from changing Price ranges provide liquidity in order to maximize your profits.
Secondly, LP token is an NFT form, if in Uniswap V2 there are many protocols that support swap, lending, yield farming for LP tokens ERC-20. When LP tokens become NFTs, which projects will support doing that? However, this is only a temporary issue and will be resolved soon.
Read more: How is Solana's On-chain analysis (SOL) ecosystem evolving?
Above is information about Uniswap V3's operating model from many sources that TraderH4 synthesizes and researches for readers. Hope to help you better understand how the project has changed after the upgrade.
According to readers, is the Uniswap V3 upgrade really effective and solves the problems of V2? Discuss with us at Telegram Group TraderH4. And don't forget to visit TraderH4's website to quickly update the upcoming events of the project. See you again in the next issue of "Active Model Analysis" of TraderH4.
Note: All information in this article is intended to provide readers with the latest information in the market and should not be considered investment advice. We hope you read the above information carefully before making an investment decision.
Today TraderH4 will analyze the operating model of SushiSwap - an AMM that integrates various business models in the decentralized financial market.
Today TraderH4 will analyze the operating model of Uniswap V2 - AMM giant in the decentralized financial market.
Ngoài PancakeSwap, hệ sinh thái BNB Chain còn có một AMM khác có TVL đạt 150 triệu USD chỉ sau hai tháng ra mắt, dự án này được gọi là Thena.
Blockade Games provides a platform that allows developers to create blockchain games. In addition, Blockade Games also creates many interesting free games.
UNQ Club is a project that provides a blockchain platform that allows investors to collect and manage existing NFT assets.
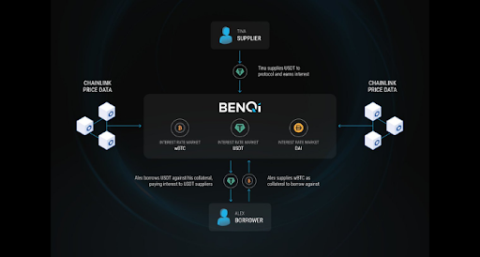
BENQI is one of the important pieces of the Avalanche ecosystem. Join TraderH4 to find out what BENQI (QI) is as well as detailed information about the QI token.
In addition to a cryptocurrency storage wallet, SafePal is also known to many investors for its SFP tokens and airdrop events with attractive rewards.
The fever from Akita Inu in the Crypto market in the past time has created a great buzz along with the rapid development of the "dog house token".
What is IoTeX? This is a blockchain built and developed in conjunction with the Internet of Things (IoT). Join TraderH4 to learn this article.
What is OKB? OKB is an exchange coin of OKX and the OKX Chain blockchain. Let's learn about OKX and OKB exchanges with TraderH4 in this article.
DROPP GG brings an innovative and novel idea to provide an NFT mint platform based on geographies outside of the real world.
CronaSwap is a DEX built on Cronos Chain, which has a similar model to Uniswap.